General
LS-OPT provides a user-defined interface to extract history and response results, respectively.
Any user-defined program, e.g. C, Fortran or Perl programs, or any post-processors, e.g. LS-PrePost may be used to extract results. The program is called from the run directories. This has to be considered if relative paths are used.
User-defined Histories
The user-defined program is used to produce a file named LsoptHistory containing xy data in a 2-column format. LS-OPT uses the file LsoptHistory only as a temporary file and stores the values in the LS-OPT database directly after the extraction. Hence defining multiple user-defined histories is not a problem, in the end, the LsoptHistory will contain the values of the last defined history.
Example:
In this example, the post-processor
LS-PrePost is used to extract a history result.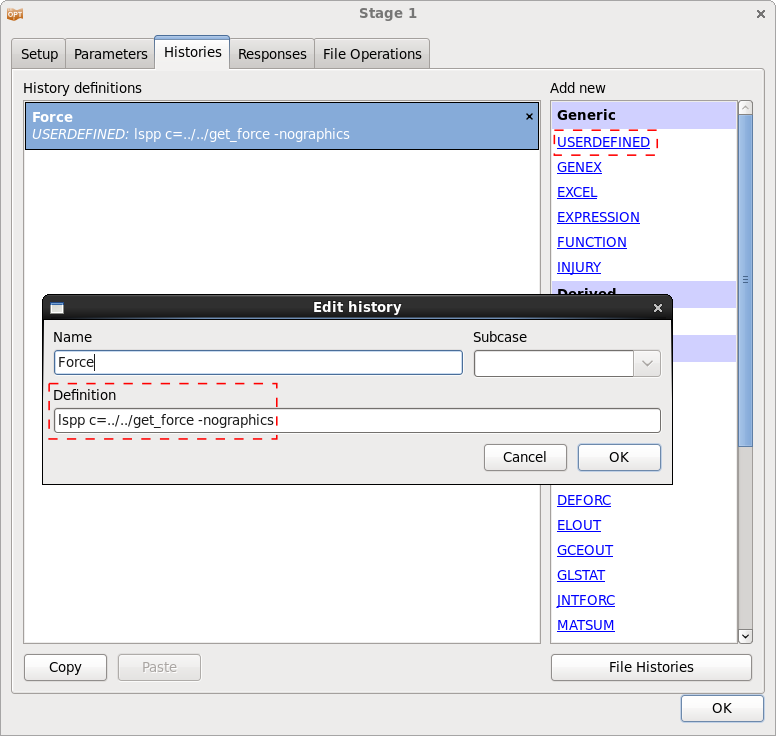
The LS-PrePost command file get_force is given below.
open d3plot d3plot ascii rcforc open rcforc 0 ascii rcforc plot 4 Ma-1 xyplot 1 savefile xypair LsoptHistory 1 deletewin 1 quit
To create the LS-PprePost command file, execute the appropriate commands in LS-PrePost. LS-PrePost saves the executed steps in the command file lspost.cfile. Make sure that the name of the output file is LsoptHistory.
User-defined Responses
The user-defined program has to output a single floating-point number to standard output.
Example:
In this example, a Perl program is used to extract a response.
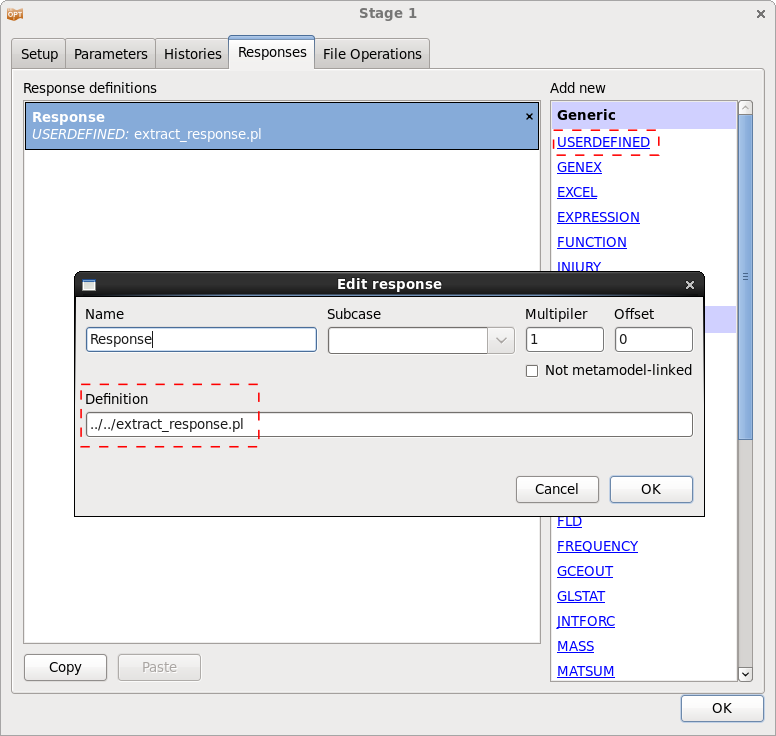
An example for a Perl program extracting a response result is given below.
#!/usr/bin/perl
# open file
open(IN,"results.txt");
$i = 0; # variable to count line number
# read file
while(<IN>){
# first value in 10th line is response value
if ($i == 10){
@output = split;
last;
}
$i++;
}
# print value to standard output
print ("$output[0]\n");
# close file
close(IN);
